Let us walk you through the ancient Roman city & its history!
VIMINACIUM is a Roman city of emperors and a legionary camp from the 1st century AD. It was located in the Roman province, Upper Moesia (Moesia Superior), which included the largest part of today's Serbia, northern Macedonia and part of northwestern Bulgaria. The city of Viminacium was located at the confluence of the river Mlava and the Danube (near today's Kostolac), 1375 km east of Rome and 95 km southeast of Singidunum.
The Danube port on Via Militaris (Military Road) and the capital of Upper Moesia (lat. Moesia Superior), which included part of today's Serbia, northern Macedonia and part of northwestern Bulgaria. The status of Municipium (a city with an independent city administration) was given during the reign of the enlightened emperor-philosopher Hadrian, at the beginning of the 2nd century AD.
One hundred years later, Viminacium received the status of a colony and approval for minting its own money.
From the beginning of the 3rd century, the city had 6,000 soldiers and more than 10,000 inhabitants. In ancient times, that fact shows that it is an important metropolis.
Emperor Septimius Severus, the same one who is remembered as a great enemy of Christians, decided to proclaim his son Caracalla emperor here. That happened 211 years ago. And that is the culmination of the mosi of the pagan Viminacium.
Thousands of researched necropolises point to an entire urbanized and extremely prosperous city. The city of Vrba is slowly rising with all its magnificent streets, squares, military camp, cousins, workshops, hippodrome, aqueduct, bathrooms, amphitheater and all other buildings that are hidden under layers of arable land, centuries of mud and dust.
What has been researched throughout the years?
To all those who have been researching this city in the last few decades, Viminacium brought a very thorough insight into the way of life in a Roman province.
What was found in this ancient city? Various items: from toys for children to figurines of gods and ancestors. Decorative utensils made of precious glass and numerous items that made up military equipment and weapons were also found. Oil lamps of various shapes and designs, jewelry, fine women's hair ornaments made of ivory and of course, the coats of famous legions. And all that was found, here, in Viminacium.
Ones who visits the remains of the spa will have a clear picture of what a state-of-the-art wellness center should look like today. The spa had public baths with swimming pools, massage rooms, a steam bath and extremely sophisticated toilets, as well as underfloor heating, which is really rare where it can be found in the more modern facilities of today.
The Romans were able to enjoy socializing while bathing in the spa. That is why these places were small "sanctuaries", extremely pleasant spaces, beautifully decorated. The spa is also known for night swimming with the lights of a hundred lamps.
Research is taking place in many fields. Fantastic new discoveries and artifacts, which they report on Chinese television.
The remains of a large port, a fantastic aqueduct and a drinking water distribution system were found in the settlement. The mausoleum hides the secrets of the Emperor Hostilian, who is buried there. An unusual destiny sealed the life of the emperor in the year 251, when he died of plague and died in Viminacium.
His brother Herenius and his father Trajan Decius were killed in the war with the Goths, so Hostilian received the throne. Hostilian's mausoleum is the central part of the necropolis in which richer and more prominent citizens were buried.
Viminacium was a place where emperors, soldiers, ancient matrons, craftsmen, artists met; they all grew up right there - in a lavish ancient metropolis.
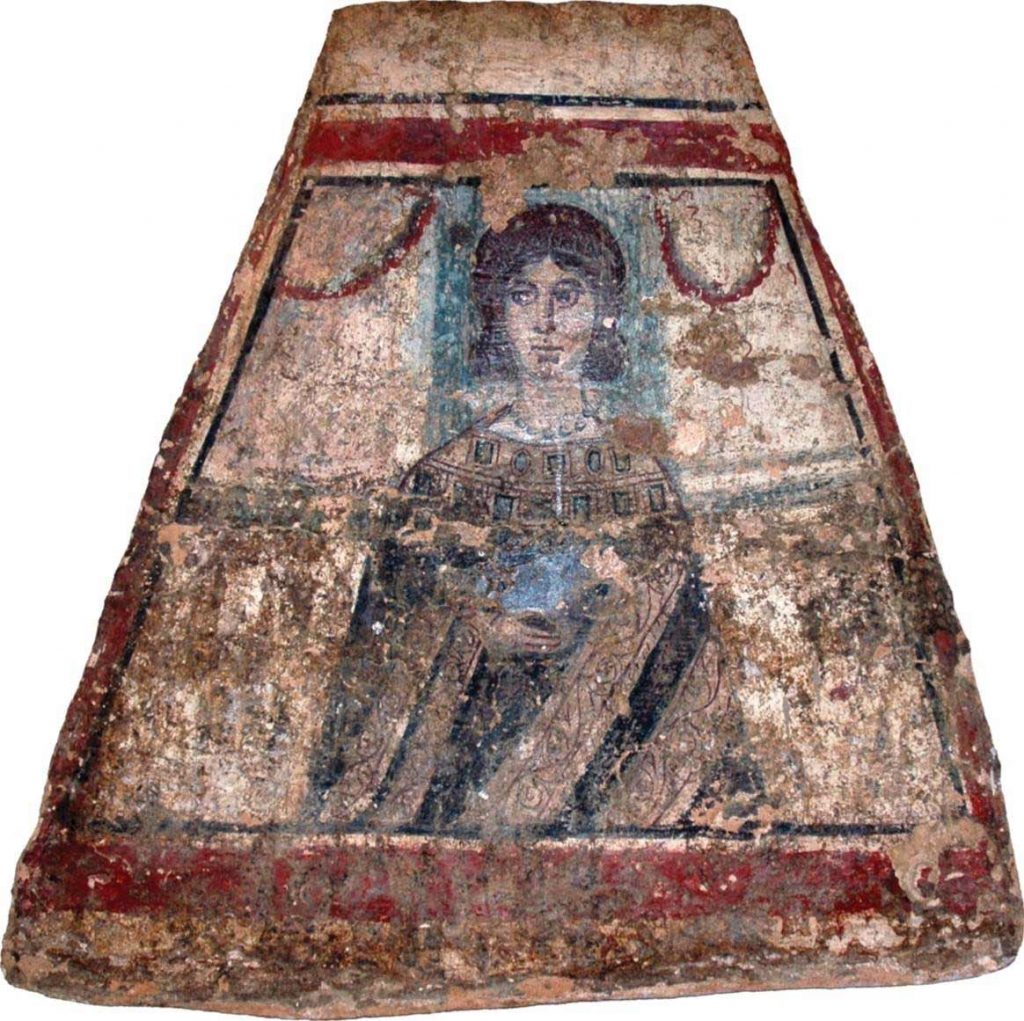

Viminacium Mona Lisa
We remember Viminacium as a city that testifies to the way of life on the Limes (Latin pl. Limites - the most common name for the fortified border of the Roman Empire). This city was walked by people who worshiped different gods, but who had something in common - they all loved comfort, beauty and luxury.
Skeletons of ten different anthropological features were found on the territory of the archeological park.
The oldest symbol of salvation and eternal life, the peacocks of paradise, was painted by a master of his craft. The question is, was it the same master who painted the enigmatically smiling face of a young woman from Viminacium?
Whether it is a paradox or not - the fact is that the thermal power plant was given the epithet "most deserving" in the process of a new phase of intensive research that began in the seventies.
We believe that there is an appropriate awareness of the competent institutions and quality cooperation between the thermal power plant and the archeological park.
Fortunately for us, Viminacium has had a prominent place in history, ancient sources and ancient chronicles.
Its founding is an introduction to the story of the legionaries who built it.
Viminacium is adorned with several frescoes of supreme artistic achievement, from a young woman with a magical smile (Mona Lisa from Viminacium as she is affectionately called) who serves bread and wine, to the most impressive frescoes with representations of earthly and celestial hunting and heavenly images filled with gorgeous peacocks colored with the magnificent blue.
In the unstoppable onslaught of the Huns, Viminacium was destroyed for the first time in 441. Only for a moment did its old glory flash later in the 6th century during the rebuilding of the city during the reign of Emperor Justinian. This Danube port has since entered the era of permanent settlement of Slavs.
Today, Viminacium is waking up from a thousand-year-old dream. It is a city that has yet to be discovered. It is one of the largest archeological parks in Europe and the only Roman city that can be completely excavated because there is no new urban settlement on the surface of the ancient city that would prevent research and excavations.
The Viminacium Science Center is known for its exceptional cultural and historical value, as a site of international importance (on the UNESCO tentative list, which means that it is on the list of those areas located in the territory of UNESCO member states that are considered to be important for inscription on the World Heritage List and this opens the way for its nomination to the World Heritage List in the coming period). It includes a scientific research center, an archeological site of a Roman city and a legionary camp from the first century AD and a paleontological park. It houses authentic buildings of ancient basilicas and necropolises, a Roman amphitheater, an aqueduct nearly 10 km long and numerous other buildings from the ancient period.
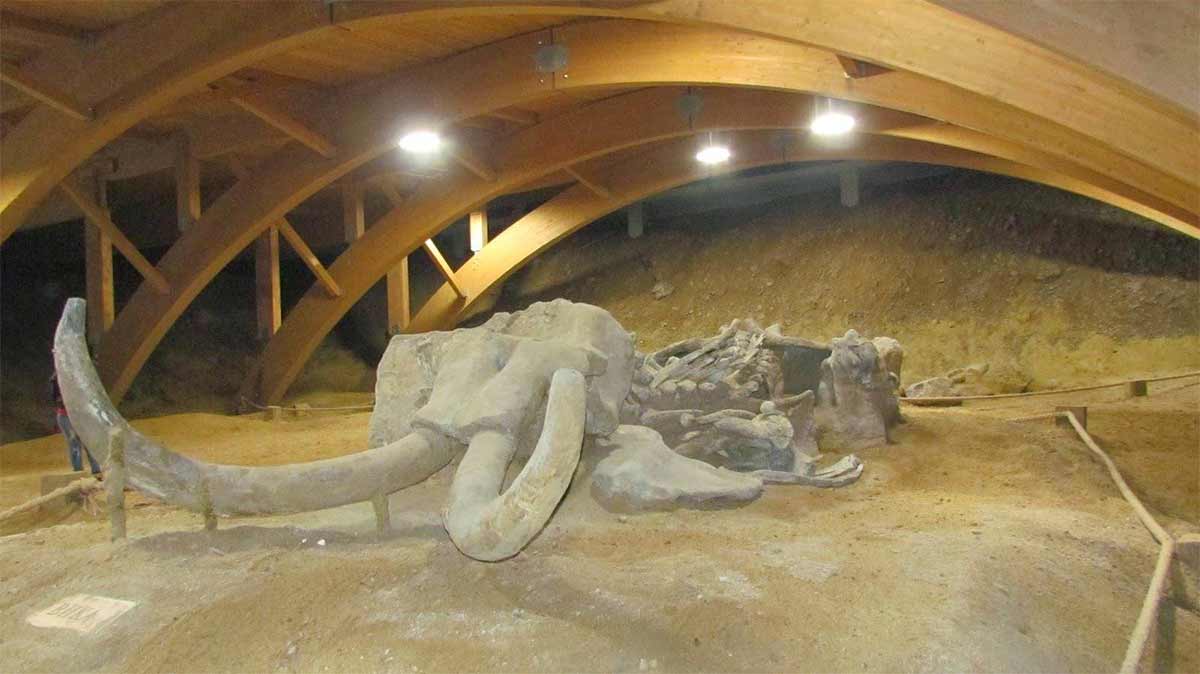
The Viminacium Science Center is also internationally known for its recently discovered extremely rare remains from the prehistoric period. A special attraction within the archeological park Viminacium is the paleontological park in which mammoths discovered in the surface mine Drmno, and on the edges of the Roman site, are presented.
The most significant find is a mammoth, preserved in its entirety, known as Vika. The skeleton was found only 350 meters east of the mausoleum, and originates from Pleistocene deposits, from a depth of 27 meters (million years) - more information at: www.viminacium.org.rs











